Setting up a domain via CNAME
Back to Dashboard
Firstly, let's define what CNAME is. Here's what the first line
Wikipedia tells us.
A Canonical Name record is a type of resource record in the Domain Name System that maps one domain name to another.
You can find a myriad of resources on what CNAME is, but the quickest way to understand is that CNAME allows you to display
a website of one URL under a different URL (or alias).
For example, if I have a website whose URL is www.my-website.com, CNAME allows me to use
www.my-different-domain.com as an alias to display the same website. The alias address will
be displayed in the browser address bar.
This is a great way for tools to offer a more personalized or customized service. Imagine you open a Shopify store whose default address could be
my-own-store-1234.shopify.com. Now if you want yo use your own domain
www.my-own-store.com for this shop, you would typically create a CNAME for it.
Let's dive deeper and see how we can create a CNAME that points to your Newsy site.
Creating a CNAME
Every site created on Newsy automatically has its own unique Newsy address
(e.g. ahsu129kasj.newsy.co). We then create a CNAME, which makes your domain an
alias to this address. The CNAME entry would look like below.
| Name | Value | TTL |
| www.my-domain.com | ahsu129kasj.newsy.co | 3600 |
To do this, please login to your domain registrar's control panel and go to the DNS settings page
of your domain and add a CNAME. Below is a screenshot of DNS settings page in GoDaddy.
Root or www?
In the above table, we created a CNAME for
http://www.my-domain.com. But what would happen if you type
http://my-domain.com?
If above table was your domain's entire DNS settings, typing
http://my-domain.com will result in an error because we haven't
defined what should happen if you type the root (or sometimes called naked) domain.
One way is to add two CNAME entries as follows and Newsy will handle resolving both correctly.
Please note that some domain registrars do not allow root-level CNAME.
| Name | Value | TTL |
| my-domain.com | ahsu129kasj.newsy.co | 3600 |
| www.my-domain.com | ahsu129kasj.newsy.co | 3600 |
Redirecting root to www
If your domain registrar does not allow you to add a CNAME entry for the root-level domain and requires you to have an
A Record
(i.e. A Record is similar to CNAME, but instead of pointing to another
URL, it points to an IP address.) you can use a free redirect service provided by GitHub, which essentially redirects all
root-level requests (http://my-domain.com) to www sub-domain
(http://www.my-domain.com). The following table shows you this set up.
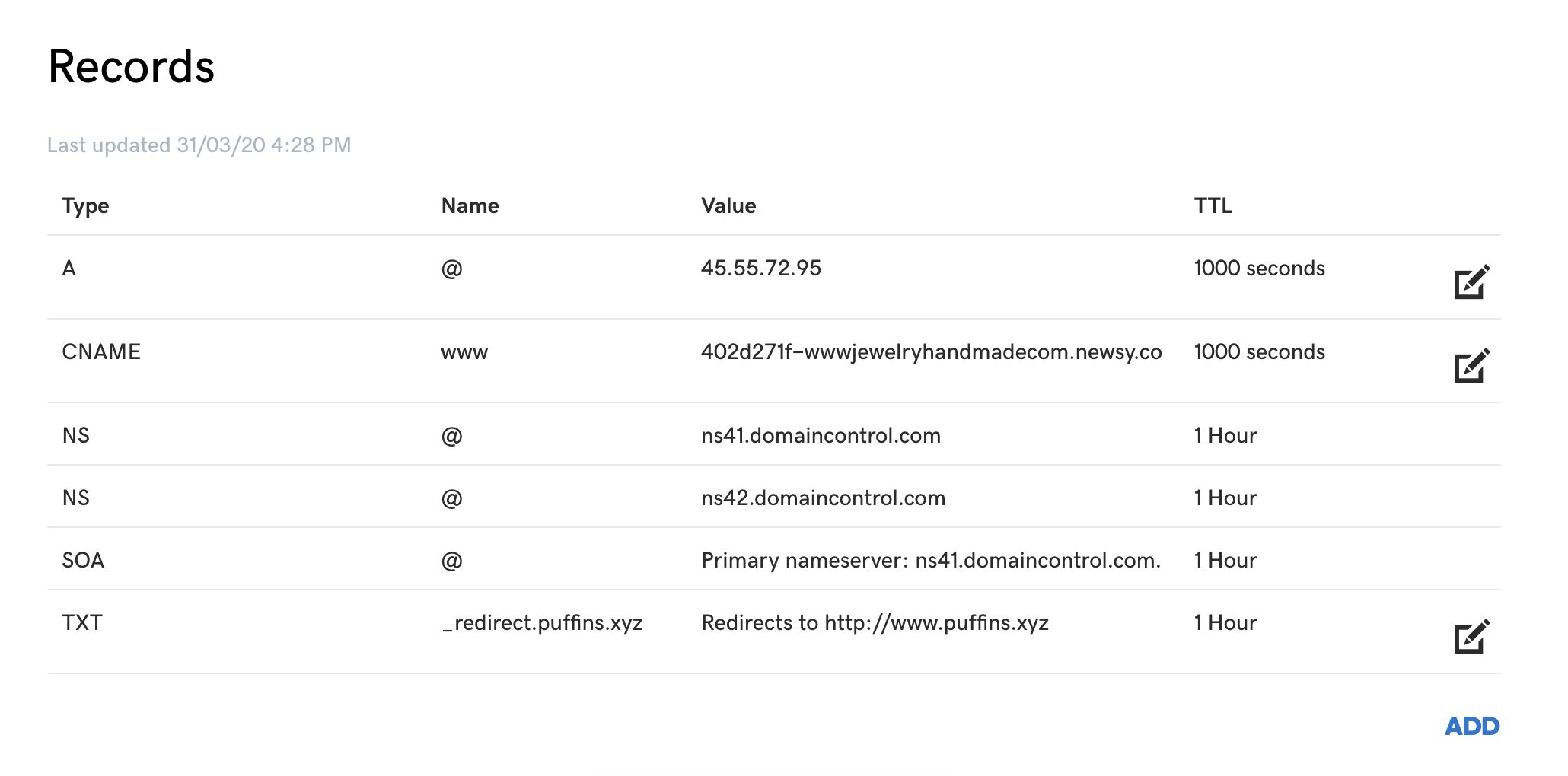
| Type | Name | Value | TTL |
| A Record | my-domain.com | 45.55.72.95 | 3600 |
| CNAME | www.my-domain.com | ahsu129kasj.newsy.co | 3600 |
| TXT | _redirect.my-domain.com | Redirects to http://www.my-domain.com | 3600 |
* This step may seem slightly hacky (and it is), but it's actually a very popular way to redirect the root-level domain to
another domain.
Some tips
Our recommendation is to use the www sub-domain
(http://www.my-domain.com)
as the main URL for your Newsy site and use the TXT record to redirect all root-level requests to www.
If you use both root-level and www, it becomes a little difficult to keep track of URLs of all your contents since every
content on your site now has two URLs.
We also strongly recommend using
CloudFlare
as your DNS server. CloudFlare's free tier is more than enough to get your site up and running and it will also help you
set up HTTPS for your domain, which we discuss in
Enabling HTTPS for your site.
Troubleshooting
Sometimes, there might be a misconfiguration at your domain registrar's level. So it's always good to double check this.
If your site is not working correctly, first please check that your domain at least responds. If you're familiar with
command line tools, you can simply type ping www.my-domain.com
to see if there any responses.
You can also try various DNS checking tools available online. We list some of them below.
DNS Checker
- Use this to check if your domain responds (similar to ping, but does from different places around the world)
Uptrends DNS
- Checks all the DNS entries for your domain.